Polyamides (PA) are polymers containing cyclic amide groups (-CONH-) as part of the polymer backbone. Polyamide was one of the first polycondensation polymers; it was first made by Carothers of DuPont in 1938 with great success as an alternative to natural fibers. They are composed of hexamethylenediamine and sebacoyl chloride. There are now different types of polyamides due to their thermal resistance and high mechanical strength.
Polyamides can be prepared with aliphatic or aromatic monomers (acids or amines). Aliphatic polyamides are generally hygroscopic materials, and the introduction of aromatic rings into the monomer structure reduces this property. Water is an important impurity when polyamide injection molding.
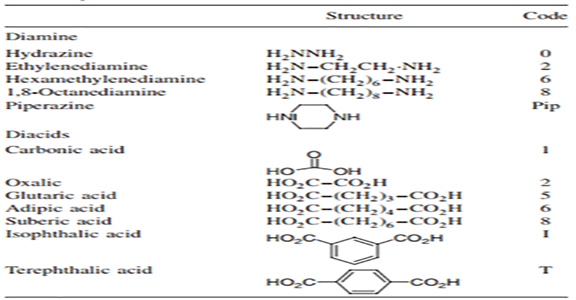
Polyamides are generally called Nylon, followed by two numbers, the first number indicates the number of carbon atoms in the diamine monomer, and the second number indicates the number of carbon atoms in the diacid monomer. If a ring is part of a polyamide, either in the amine or acid part, the initials of the ring name must be used. Also, if the polyamide is derived from an amino acid, only one number is needed to describe the number of carbon atoms between the two functional groups. These rules are shown in Table Codes to be Used with the Different Polyamides in the Nylon Nomenclature:
Without polyimide materials, there would be no progress in modern science and technology; polyimide has had a significant impact on the development of various fields of science and technology.
Polyimides are widely used in films, fibers, foams, films, plastics, composites, glues, adhesives and coatings, and are used in the manufacture of various structures, units and components that operate under extreme temperature conditions and coating. One of the key areas of application of polyamides is membrane technology, especially in gas treatment technology and energy storage.
Polyimide can be prepared by several step growth processes. One of the most common methods for this purpose is the reaction of dianhydrides with diamines (Figure 3.6). The first product obtained is polyamic acid, which has the advantage of being soluble in organic solvents (usually aprotic polar solvents such as dimethyl sulfoxide, DMF, dimethylacetamide and NMP are used). The polyamic acid solution is easy to handle and process. This acid can be thermally cycled to form polyamides, which are insoluble in most common organic solvents.
Dema commits to create value for our clients, provide solutions of polymer raw materials, like PP, PE, PVC, PET, PA,ABS and FIBC bags, and help you occupied a competitive position in your market. You are welcome to contact us at any time, we will serve you wholeheartedly.
