Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP) are two of the most widely used thermoplastic polymers for film applications. While both materials are similar in some ways, they have distinct differences in terms of chemical structure, properties, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right material for various industrial and packaging needs. This article explores the key differences between PE and PP film grades.
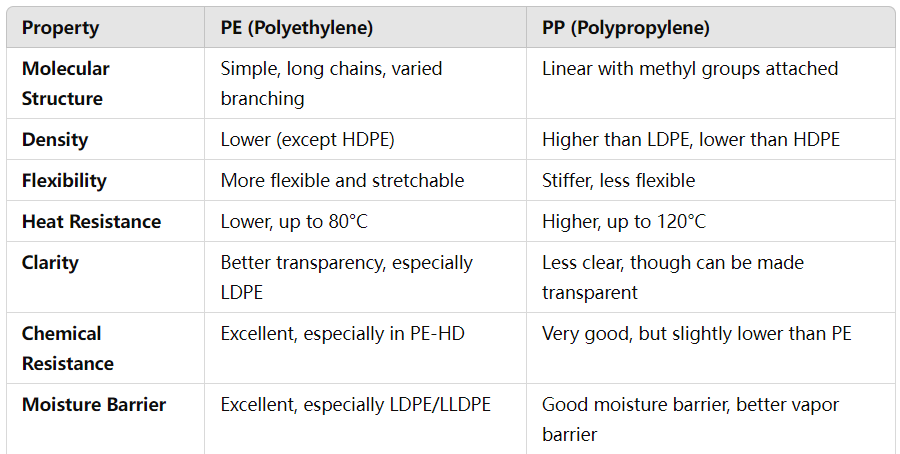
PE (Polyethylene): PE is a polymer made from the polymerization of ethylene monomers. It has a relatively simple structure consisting of long chains of carbon atoms with attached hydrogen atoms. PE comes in different forms, including LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), and LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene), which offer different characteristics based on the arrangement of their molecular structure.
PP (Polypropylene): PP is made from the polymerization of propylene monomers. It has a more complex structure than PE, with alternating carbon and hydrogen atoms and a methyl group (CH3) attached to every other carbon atom. This additional side group gives PP its unique properties.
PE: The density of PE films can vary depending on the type of PE (LDPE, HDPE, or LLDPE). LDPE has a lower density with more branching, while HDPE has a higher density and a more crystalline structure. PE is generally softer and less rigid compared to PP.
PP: Polypropylene has a higher density than most types of PE, but lower than HDPE. Its higher molecular weight results in a more rigid and crystalline structure, making it stiffer and more heat-resistant than PE.
PE: PE films are known for their flexibility and elongation properties, which make them suitable for applications like stretch wrap and plastic bags. PE, especially LDPE and LLDPE, is softer and can stretch without breaking, making it ideal for products requiring flexibility.
PP: PP films are stiffer, more rigid, and have a higher tensile strength than PE films. They also have better resistance to stress and are more crack-resistant. However, PP films are less flexible and tend to break or crack under high stress, especially at low temperatures.
PE: PE films have lower heat resistance than PP films. LDPE and LLDPE can withstand temperatures up to around 80°C (176°F), while HDPE can handle slightly higher temperatures. PE begins to soften and deform under higher heat, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications.
PP: PP films have superior heat resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, typically around 100-120°C (212-248°F) without deforming. This makes PP a better choice for applications requiring heat resistance, such as microwaveable containers and food packaging that may come into contact with hot substances.
PE: LDPE and LLDPE films are generally more transparent and have better clarity than PP films. This makes PE suitable for applications where the contents need to be visible, such as food packaging, shrink films, and certain types of plastic bags.
PP: PP films, while they can be made translucent, generally have less clarity than PE films, especially in thicker applications. However, PP can be made into clear films for packaging applications that require a stiffer, more rigid material.
PE: PE has excellent chemical resistance to many acids, bases, and organic solvents. It is widely used in chemical storage containers, liners, and packaging for items that may be exposed to harsh chemicals.
PP: PP also has good chemical resistance, particularly to organic solvents, acids, and bases. However, it may be slightly more susceptible to certain chemicals compared to PE. Despite this, PP's chemical resistance is generally sufficient for most applications, including food packaging and medical products.
PE: PE, especially LDPE and LLDPE, is an excellent moisture barrier, making it ideal for packaging products that require protection from humidity and water, such as food and agricultural products. It is often used in films for food packaging and stretch wrap for moisture-sensitive goods.
PP: PP also has good moisture barrier properties, but in general, it provides better vapor barrier performance than PE. This makes PP a preferred material for packaging where the preservation of freshness is crucial, such as snack food packaging, coffee pouches, and pharmaceutical packaging.
PE: Due to its flexibility, softness, and cost-effectiveness, PE is widely used in applications such as:
Plastic bags (grocery, trash, produce)
Stretch and shrink wraps
Food packaging
Agricultural films
Liners and packaging films
PP: Because of its rigidity, heat resistance, and chemical properties, PP is used in:
Food packaging (especially for microwaveable products)
Pharmaceutical packaging
Automotive parts
Rigid containers and bottles
Nonwoven fabrics (such as those used in hygiene products and medical masks)
Luoyang Dema Import & Export Co., Ltd. aims to provide high-quality, cost-effective products for global factories, plastic product manufacturers, and material distributors. Luoyang Dema Import & Export Co., Ltd. provides the best PP, PE, PVC, PET, EVA, ABS, and POM material solutions for plastic product manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, distributors, factory owners, processing workshops, etc.
If you are looking for general plastic materials, please feel free to get the latest prices and quotations from Luoyang Dema Import & Export Co., Ltd. The sales team will reply within 48 hours.
